Explore the pros and cons of rooftop vs. ground-mounted solar panels. This guide helps you make an informed choice based on space, cost, and efficiency.
Have you ever wondered which type of solar panel installation is best for your situation: rooftop or ground-mounted? Choosing the right option can be a bit overwhelming, given the variety of factors involved.
Understanding Solar Panel Types
Solar panels come in various configurations, but the main types are rooftop and ground-mounted systems. Each type has unique advantages and drawbacks, depending on your needs, space availability, and local regulations.
What are Rooftop Solar Panels?
Rooftop solar panels are installed directly on the roofs of buildings. This option is popular among homeowners because it utilizes existing structures, saving precious land space. If your roof has a south-facing orientation and sufficient sunlight exposure, this method may be ideal for you.
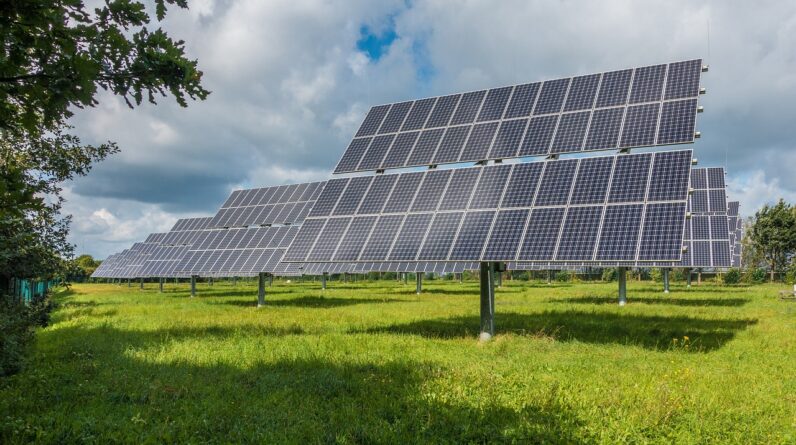
What are Ground-Mounted Solar Panels?
Ground-mounted solar panels are installed on the ground, usually in open spaces or backyards. This installation type allows for more flexibility in terms of panel orientation and positioning. If you own a substantial amount of land with plenty of sunlight, you may prefer this option.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Rooftop and Ground-Mounted Solar Panels
In deciding between these two types of solar panel installations, several factors come into play. Consider the following:
Space Availability
One of the first things to look at is how much space you have available for your solar installation.
- Rooftop Installations: If you’re short on land space or live in an urban area, rooftop solar panels might be the most feasible choice.
- Ground-Mounted Installations: If you have ample land, you can take advantage of ground-mounted installations, which can often accommodate more panels.
Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight exposure is crucial for maximizing energy production.
- Rooftop Systems: Factors like shading from trees or nearby buildings can affect energy generation.
- Ground-Mounted Systems: These can be positioned strategically to ensure maximum sunlight throughout the day without obstructions.
Aesthetics
The visual appeal of your solar installation can play a significant role in your decision.
- Rooftop Panels: While discreet, they may not be to everyone’s liking. Some people appreciate how they blend into the roofline, while others may find them unappealing.
- Ground-Mounted Panels: These can be designed to be more visible, and while some people appreciate their functionality, others might see them as a blight on the landscape.
Local Regulations and Restrictions
Before choosing a type of solar installation, it’s essential to be aware of local building codes and regulations.
- Rooftop Installations: Typically face fewer zoning restrictions. However, you may need to adhere to guidelines concerning height, materials, and structural integrity.
- Ground-Mounted Installations: Often subject to more stringent regulations, especially concerning land use and disturbance of the natural environment.
Costs and Incentives
Understanding the financial aspect of solar panel installation can help you make an informed decision.
| Aspect | Rooftop Solar Panels | Ground-Mounted Solar Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Costs | Often lower due to fewer structural requirements | Higher due to the need for mounting equipment and installation |
| Maintenance Costs | Generally lower, as they are usually harder to access | Potentially higher due to accessibility issues |
| Incentives and Rebates | May qualify for special programs at local and federal levels | Similar programs might apply but vary by location |
If budget considerations are a priority, you should weigh these factors carefully.
Installation Time
The installation time can influence your choice, especially if you’re eager to harness solar energy quickly.
- Rooftop Installations: Generally quicker to install, as they often require less preparatory work.
- Ground-Mounted Installations: Might take longer due to land preparation, including level adjustments or grading.
Flexibility and Scalability
If you’re considering future expansion of your solar energy system, it’s worth noting the flexibility both options offer.
- Rooftop Panels: Expansion can be limited by available roof space. It might mean adding a new roof section if you need more panels.
- Ground-Mounted Panels: These systems typically offer more flexibility, allowing for future expansions without major structural changes.
Maintenance Requirements
After installation, maintaining your solar panels is key to long-term efficiency.
- Rooftop Systems: These can accumulate dirt, debris, and even snow. Regular cleaning might be challenging, but typically they require less maintenance.
- Ground-Mounted Systems: Easier to access for cleaning and routine maintenance checks. However, they can be affected by surrounding vegetation and wildlife.

Pros and Cons of Rooftop Solar Panels
Analyzing the pros and cons can aid in your decision-making process.
Advantages
- Space Efficiency: Roof installations free up ground space for other use.
- Faster Installation: Typically easier and quicker to set up.
- Lower Costs: Usually have lower installation costs if no roof reinforcement is needed.
Disadvantages
- Limited Expansion: Restricted by the available roof area.
- Potential Shading Issues: Nearby trees or buildings may obstruct sunlight.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Some may find them visually unappealing on their homes.
Pros and Cons of Ground-Mounted Solar Panels
Just like rooftop systems, ground-mounted installations come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Maximized Sunlight Exposure: Better positioning without rooftop obstructions enhances energy production.
- Easier Maintenance: Making access for cleaning and repairs more straightforward.
- More Scalability: Easier to add panels later if you choose.
Disadvantages
- Space Requirements: Require a significant amount of land, which might not be available to everyone.
- Higher Initial Costs: Installation can be more expensive than rooftop setups.
- Zoning Restrictions: Local regulations can limit where you can place them.
Environmental Concerns
When opting for solar energy, being mindful of its environmental impact is important.
Rooftop Panels
- Land Preservation: Using a rooftop means you’re not utilizing extra land that could support natural habitats.
- Reduced Urban Heat Islands: Installation could aid in cooling your home, fighting the urban heat effect.
Ground-Mounted Panels
- Land Use Impact: Ground-mounted systems can disrupt local ecosystems. This is particularly significant if you’re installing panels on a previously untouched area.
- Wildlife Considerations: Construction in natural areas may disturb local wildlife. Thoughtful planning can mitigate this.
Determining the Best Option for Your Needs
After weighing these factors, the question remains: which option suits your lifestyle, budget, and energy needs?
Assess Your Goals
Take your time to clarify what you hope to achieve with solar energy. Whether it’s financial savings, boosting property value, or increasing your sustainability credentials, your goals will shape your choice.
Take a Look at Your Property
Spend time observing your home and land. Consider sunlight patterns throughout the day and check out your roof’s condition or available land area.
Consultation with Professionals
Having a conversation with solar energy professionals can further guide you. They can assess your property, answer questions, and provide tailored recommendations based on your specific conditions.
Real-World Examples
Sometimes seeing how others have navigated this decision can help clarify your path.
Example: Rooftop Installation Success
Imagine a suburban family with a south-facing roof. They decided to install rooftop panels, which not only provided significant energy savings but also blended seamlessly with their home’s design. They were able to expand energy production without taking more land.
Example: Ground-Mounted Installation Triumph
Consider a rural entrepreneur with vast land suitable for farming and solar energy. They chose ground-mounted panels, maximizing their energy production without sacrificing their farmland. This setup offered them room for future expansions, making it a long-term investment for their operations.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for You
Ultimately, your decision hinges on your unique circumstances. By weighing the benefits and drawbacks of both rooftop and ground-mounted solar panels, considering space and sunlight exposure, assessing costs, and consulting professionals, you’ll pave the way for a well-informed decision.
Whether you opt for rooftop or ground-mounted solar panels, embracing solar energy can lead to substantial savings and significant environmental benefits in the long run. You’re contributing to a more sustainable future by harnessing the sun’s power, no matter which installation type you choose.